After years of rollbacks, democracy movement making gains in the states
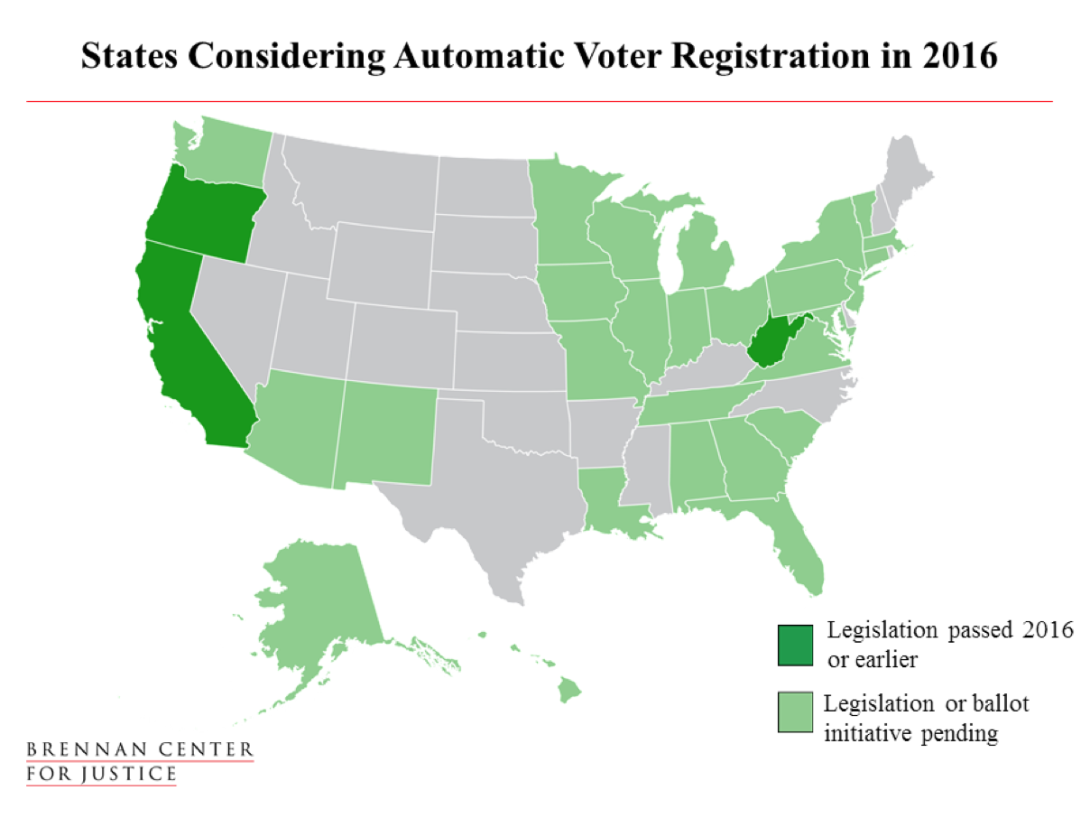
The most popular pro-democracy reform now being implemented at the state level is automatic voter registration. Twenty-eight states are considering it this year, including eight in the South. (Map from the Brennan Center for Justice.)
More than 1,400 people were arrested during protests in Washington, D.C., over the past week as part of Democracy Awakening and Democracy Spring, a grassroots movement calling for an end to money's chokehold on U.S. politics and for restoration of voting rights.
The protests represented one of the biggest acts of civil disobedience in recent U.S. history. Among those arrested were actress Rosario Dawson, Ben Cohen and Jerry Greenfield of Ben & Jerry's ice cream, and Miss New Jersey U.S. Sameera Khan, who wore her sash to the protests. Participants called on Congress to pass legislation restoring the Voting Rights Act, modernizing voter registration, overturning the Supreme Court's Citizens United decision loosening limits on political money, and encouraging small-dollar political contributions through matching funds.
But while attention has been focused on the need for reform in Washington, efforts to promote democracy at the state level have been advancing as well — and producing results across the nation and the South.
A new analysis of state voting laws by the Brennan Center for Justice found that, for the fourth year in a row, bills to expand voters' access to the ballot box have outpaced those restricting voting, in terms of both introduction and passage.
As of last month, the analysis found, at least 77 bills to restrict access to registration and voting were introduced or carried over from the prior session in 28 states. But at least 422 bills to improve voting access were introduced or carried over in 41 states and the District of Columbia.
One of the major trends identified by the Brennan Center is the growing popularity of automatic voter registration. Earlier this month in West Virginia, for example, Gov. Earl Ray Tomblin (D) signed into law a measure that will allow eligible citizens who get or renew a driver's license to be automatically registered to vote, unless they opt out. West Virginia was the first state in the South to adopt automatic voter registration and the third nationwide after California and Oregon.
In all, 28 states and the District of Columbia have considered automatic voter registration this year, including eight states in the South. Besides West Virginia, they are Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, South Carolina, Tennessee and Virginia. Earlier this year, President Obama called on state legislators to make automatic voter registration "the new norm across America."
Another reform making gains in the states is online voter registration. At least 15 states considered online voter registration, with Tennessee prepared to pass it into law this session. Most states now offer some form of online registration, including Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, South Carolina, Virginia and West Virginia.
The second-most popular type of reform after registration modernization was restoring voting rights to people with felony convictions, with 27 bills introduced in 15 states. Last week Kentucky Gov. Matt Bevin (R) signed into law a bill that will make it easier for felons to have their records expunged and their voting rights restored. The previous governor, Democrat Steve Beshear, had restored felon voting rights by executive order before leaving office, but Bevins struck down the order, arguing that it was important for the legislature to play a part in changing the law. And though it wasn't done through legislation, this week Virginia Gov. Terry McAuliffe (D) issued an executive order restoring voting rights to about 200,000 convicted felons.
The trend toward expanding the franchise represents the pendulum swinging in the other direction. After the 2010 election, which saw historic Republican gains in legislatures nationwide, state lawmakers began introducing hundreds of measures making it harder to vote. In all, 22 states — including most in the South — have put new restrictions in place since then.
In 17 of those states, this presidential election will be the first one held under the new restrictions. They include Alabama, Georgia, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas and Virginia. And those restrictions are already affecting elections: For example, North Carolina's new voting law, considered one of the nation's most restrictive, led to widespread confusion during last month's primary.
While states are now passing fewer restrictive voting laws, voter ID laws are the most common type they're considering, with 37 such bills introduced or carried over into the 2016 session in 19 states. However, Florida made its voter ID law less restrictive by adding several forms of ID to its list of acceptable ones.
Tags
Sue Sturgis
Sue is the former editorial director of Facing South and the Institute for Southern Studies.
